The Right Hand Rules were created by scientists to help us predict how magnetic forces act. They are called the Right Hand Rules because they involve using your right hand.
 Right Hand Rule #1
Right Hand Rule #1: for conventional current flow. Grasp the conductor with the thumb of the right hand pointing in the direction of conventional, or positive (+), current flow. The curved fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field around the conductor.
 Right Hand Rule #2
Right Hand Rule #2: for conventional current flow. Grasp the coiled conductor with the right hand such that the curved fingers point in the direction of conventional, o positive (+), current flow. The thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field within the coil. Outside the coil, the thumb represents the north (N) end of the electromagnet produced by the coil.
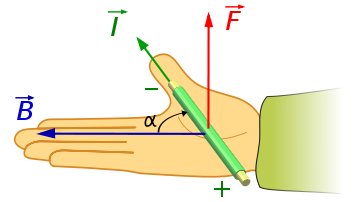 Right Hand Rule #3
Right Hand Rule #3: for conventional current flow: The motor principle. open the right hand so that the fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field (from north to south). Rotate the hand so that the thumb points in the direction of conventional (+) current flow. The orientation of the palm indicates the direction of the force produced.